ATLAS
FLORAE EUROPAEAE
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and
Military Grid Reference System (MGRS)
The AFE grid is modified from the Military Grid Reference
System (MGRS). The MGRS itself is an alphanumeric version of a
numerical UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) or UPS (Universal
Polar Stereographic) grid coordinate. Here is a short explanation
of the UTM and MGRS.
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
- Projection: Transverse Mercator (Gauss-Krüger type) in
zones 6° wide.
- Longitude of Origin: Central meridian (CM) of each
projection zone (3°, 9°, 15°, 21°, 27°, 33°, 39°,
45°, 51°, 57°, 63°, 69°, 75°, 81°, 87°, 93°,
99°, 105°, 111°, 117°, 123°, 129°, 135°, 141°,
147°, 153°, 159°, 165°, 171°, 177°, E and W).
- Latitude of Origin: 0° (the Equator).
- Unit: Meter.
- False Northing: 0 meters at the Equator for the Northern
Hemisphere; 10,000,000 meters at the Equator for the
Southern Hemisphere.
- False Easting: 500,000 meters at the CM of each zone.
- Scale Factor at the Central Meridian: 0.9996.
- Latitude Limits of System: From 80°S to 84°N.
- Limits of Projection Zones: The zones are bounded by
meridians, the longitudes of which are multiples of 6°
east and west of the prime meridian.
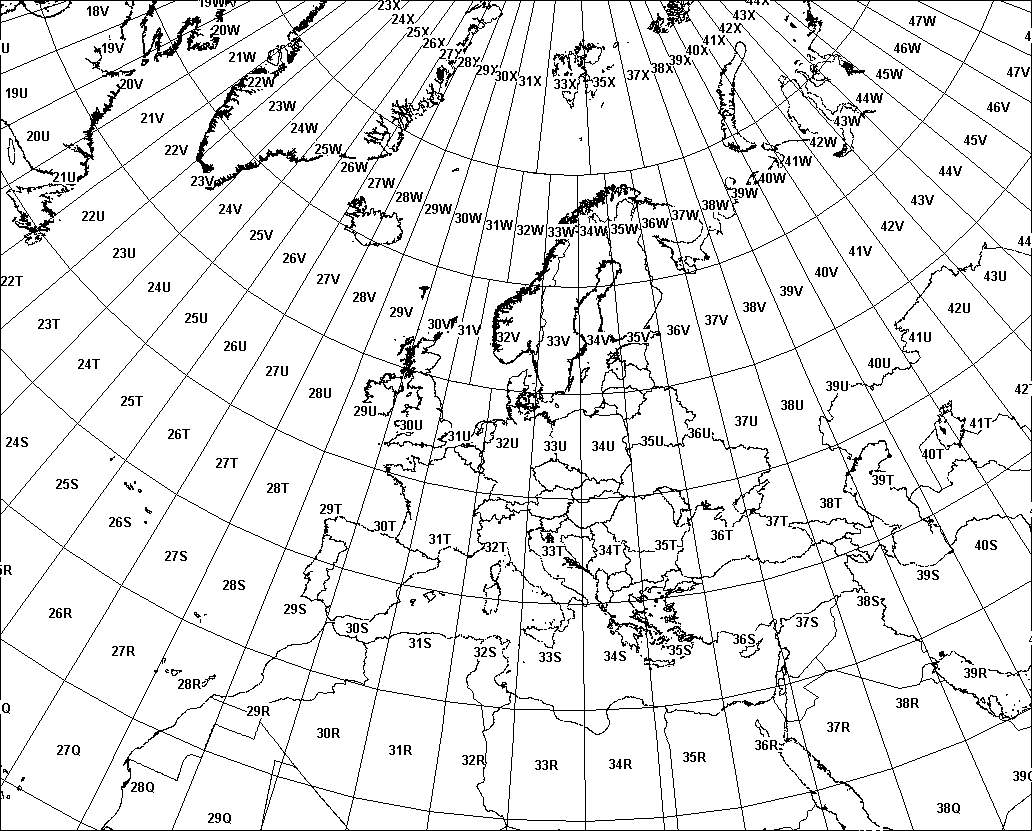
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinates define two
dimensional, horizontal, positions. The sixty UTM zone numbers
designate 6 degree wide longitudinal strips extending from 80
degrees South latitude to 84 degrees North latitude. UTM zone
characters are letters which designate 8 degree zones
extending north and south from the equator. Beginning at 80°
south and proceeding northward, twenty bands are lettered C
through X, omitting I and O. These bands are all 8° wide except
for bond X which is 12° wide (between 72-84 N).
There are special UTM zones between 0 degrees and 36 degrees
longitude above 72 degrees latitude and a special zone 32 between
56 degrees and 64 degrees north latitude:
- UTM Zone 32 has been widened to 9° (at the expense of
zone 31) between latitudes 56° and 64° (band V) to
accommodate southwest Norway. Thus zone 32 it extends
westwards to 3°E in the North Sea.
- Similarly, between 72° and 84° (band X), zones 33 and
35 have been widened to 12° to accommodate Svalbard. To
compensate for these 12° wide zones, zones 31 and 37 are
widened to 9° and zones 32, 34, and 36 are eliminated.
Thus the W and E boundaries of zones are 31: 0 - 9 E, 33:
9 - 21 E, 35: 21 - 33 E and 37: 33 - 42 E.
Military Grid Reference System (MGRS)
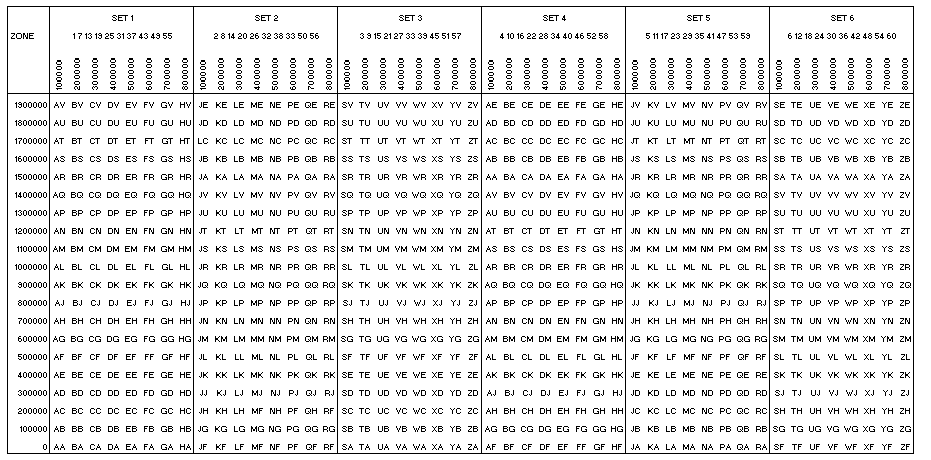
The MGRS scheme (also available as an Excel table)
The Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) is an extension of
the UTM system. UTM zone number and zone character are used to
identify an area 6 degrees in east-west extent and 8 degrees in
north-south extent. UTM zone number and designator are followed
by 100 km square easting and northing identifiers. The system
uses a set of alphabetic characters for the 100 km grid squares.
Starting at the 180 degree meridian the characters A to Z
(omitting I and O) are used for 18 degrees before starting over.
From the equator north the characters A to V (omitting I and O)
are used for 100 km squares, repeating every 2,000 km. Northing
designators normally begin with 'A' at the equator for odd
numbered UTM easting zones.
For even numbered easting zones the northing designators are
offset by five characters, starting at the equator with 'F'.
South of the equator, the characters continue the pattern set
north of the equator. Complicating the system, ellipsoid
junctions (spheroid junctions in the terminology of MGRS) require
a shift of 10 characters in the northing 100 km grid square
designators. Different geodetic datums using different reference
ellipsoids use different starting row offset numbers to
accomplish this.
If 10 numeric characters are used, a precision of 1 meter is
assumed. 2 characters imply a precision of 10 km. From 2 to 10
numeric characters the precision changes from 10 km, 1 km, 100 m
10 m, to 1 m.
MGRS 100,000-METER SQUARE IDENTIFICATION
- The 100,000-meter columns, including partial columns
along zone, datum, and ellipsoid junctions, are lettered
alphabetically, A through Z (with I and O omitted), north
and south of the Equator, starting at the 180° meridian
and proceeding easterly for 18°. The alphabetical
sequence repeats at 18° intervals.
- To prevent ambiguity of identifications along ellipsoid
junctions changes in the order of the row letters are
necessary. The row alphabet (second letter) is shifted
ten letters. This decreased the maximum distance in which
the 100,000-meter square identification is repeated.
- The 100,000-meter row lettering is based on a 20-letter
alphabetical sequence (A through V with I and O omitted).
This alphabetical sequence is read from south to north,
and repeated at 2,000,000-meter intervals from the
Equator.
- The row letters in each odd numbered 6° grid zone are
read in an A through V sequence from south to north.
- In each even-numbered 6° grid zone, the some lettering
sequence is advanced five letters to F, continued
sequentially through V and followed by A through V.
- The advancement or staggering of row letters for the
even-numbered zones lengthens the distance between
100,000-meter squares of the same identification.
- Deviations from the preceding rules were mode in the
past. These deviations were an attempt to provide unique
grid references within a complicated and disparate
world-wide mapping system.
- Determination of 100,000-meter grid square identification
is further complicated by the use of different
ellipsoids.
THE MILITARY GRID REFERENCE
The MGRS coordinate for a position consists of a group of
letters and numbers which include the following elements:
- The Grid Zone Designation.
- The 100,000-meter square letter identification.
- The grid coordinates (also referred to as rectangular
coordinates); the numerical portion of the reference
expressed to a desired refinement.
- A reference is written as an entity without spaces,
parentheses, dashes, or decimal points.
Examples:
- 18S (Locating a point within the Grid Zone Designation)
- 18SUU (Locating a point within a 100,000-meter square)
- 18SUU80 (Locating a point within a 10,000-meter square)
- 18SUU8401(Locating a point within a 1,000-meter square)
- 18SUU836014(Locating a point within a 100-meter square)
To satisfy special needs, a reference can be given to a
10-meter square and a 1-meter square as:
- 18SUU83630143 (Locating a point within a 10-meter square)
- 18SUU8362601432(Locating a point within a 1-meter square)
References:


