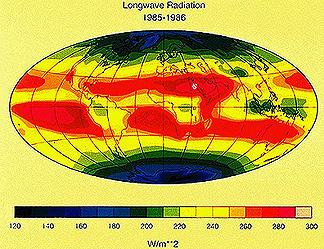
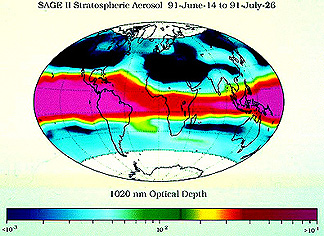


The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) was launched from
a Shuttle (STS-48) on September 12, 1991 with 10 instruments including
MLS (Microwave Limb Sounder), HRDI (High Resolution Doppler Imager),
and ISAMS (Improved Stratospheric and Mesospheric Sounder). On
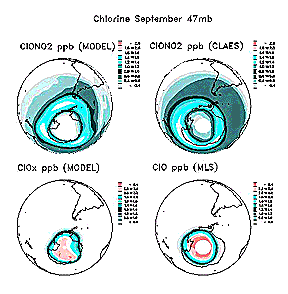
the top are plots of distribution around the south pole of ClO
and NO2 in terms of predictive models and actual results from the MLS
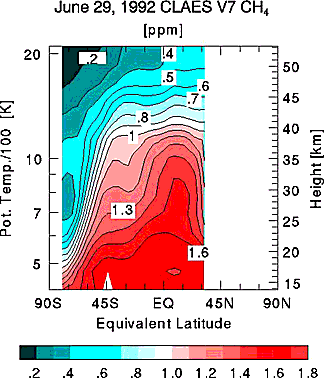
and CLAES (Cryogenic Limb Array Etalon Spectrometer); on the bottom
is a CLAES plot of CH4 (methane) distribution through the atmosphere along a specific orbit.
ADEOS (Advanced Earth Observation Satellite) is a Japanese spacecraft
launched on August 17, 1996 to conduct land, sea, and atmospheric
studies using ten instruments supplied by NASA, NOAA, NASDA (Japan)
and CNES (France) (it is now becoming common to "piggy-back" sensors
from several nations on a given satellite). Among these are NSCAT
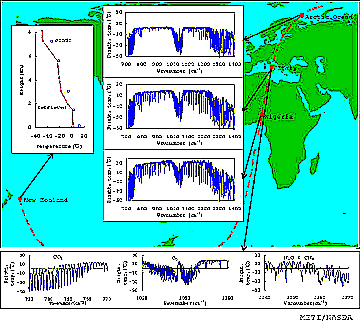
(a NASA Scatterometer) and TOMS. Examples of sounder plots using
instruments supplied by two Japanese agencies are shown below:
IMG (Interferometer for Monitoring of Greenhouse gases), looks
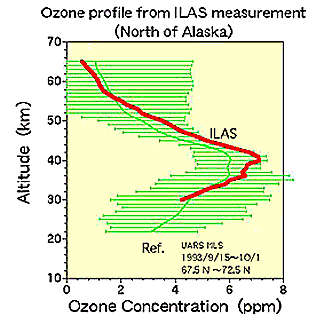
at absorption bands for CO2, CH4, H2O, O3, and NO2 in a 0.715-2.0 µm channel, CO in a 2.0-2.5 µm channel, and CH4 in a 2.32-3.05 µm channel; the ILAS (Infrared Limb Atmospheric
Spectrometer) examines ozone distribution.
Code 935, Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA
Written by: Nicholas M. Short, Sr. email: nmshort@epix.net
and
Jon Robinson email: Jon.W.Robinson.1@gsfc.nasa.gov
Webmaster: Bill Dickinson Jr. email: rstwebmaster@gsti.com
Web Production: Christiane Robinson, Terri Ho and Nannette Fekete
Updated: 1999.03.15.