Laser is a shortened term for light amplification by stimulated
emission of radiation. A typical solid laser device is a chromium-doped
ruby (Al2O3). When an external source of radiation (as from an enclosing
flash tube) acts on a shaped (usually cylindrical) ruby crystal,
one end of which is silvered to act as a mirror, the chromium
(Cr) ions dispersed in its lattice are excited to a new energy
state (electrons raised to some new orbital level), The laser
state is generated by stimulated emission when the electrons drop
back to a lower energy level (remember, from the Introduction,
the formula: E = hc/). Much of the light passes sidewards out of the crystal but light
moving along the axial zone of the cylinder encounters other Cr
ions as it undergoes repeated reflections, further exciting them
and causing a buildup or amplification, called optical pumping,
of light energy until discharged as a pulse (controlled by the flash lamp) of intense coherent
radiation at some discrete wavelength (actually a narrow frequency
range; for the ruby laser the light is pinkish) that is collimated to form a unidirectional beam which
can be aimed. Other laser materials include gallium arsenide and
excited gases such as neon or helium. Both visible and infra-red
wavelength light can be generated in this way.
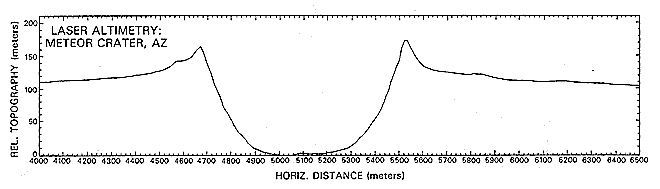
Laser altimetry has been conducted from aircraft platforms for several decades. Timing devices allow extremely precise determination of transit times, so that accuracies of a few centimeters in determining elevations (and their differences or relief) along the traverse are attainable. Aircraft can be scheduled to fly in good weather, offsetting the main disadvantage of using lasers coming from cloud interference with the light beam. An example is this profile over Meteor Crater in Arizona (see Section 18) obtained from a NASA mission (courtesy: J. Garvin):
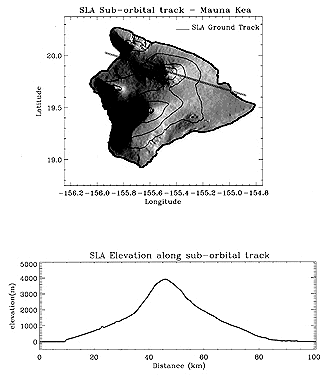
Laser altimeters are beginning to be flown on space vehicles. The Orbital Profiling Laser Altimeter is a pulsed, time-of-flight optical (1.024 µm) sensor that sends 10 pulses per second (pps) in a narrow beam (footprint 30-150 m diameter; sampling in 150 to 700 m [492-2296 ft] intervals). Operated on the Shuttle Endeavor in January, 1996, it achieved a vertical precision of 0.75 m [29.5 inches]. Each laser shot fired has a dwell time of only 2-10 nanoseconds, within the 1-10 nsec resolution of the timing electronics; with this rapid return rate, ground positions are readily determinable provided space vehicle position is known. Here is a typical profile, obtained during a pass over the volcano Mauna Kea on the big island of Hawaii:
Essentially the same sensor has been launched as the Mars Global Altimeter to the Red Planet at the end of 1996. A dedicated satellite (ALT) in the EOS series (see Section 16), scheduled for launch in the year 2003, will mount the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) designed to measure ice-sheet topography as well as cloud and atmospheric properties, but will also survey selected land and water surfaces. The 40 pulse/sec beam is generated from a neodymium:yttrium-aluminum- garnet (Nd:YAG) crystal producing a two level emergy output :1.064 µm (infrared) for surface surveys and a 0.532 µm signal for atmospheric (clouds and aerosols) measurements. Each pulse will spread over a ground spot of 70 meters (230 ft), with separation between pulses amounting to 170 m (558 ft). From its 705 km (440 miles) orbital altitude, the instrument can measure height differences on the ice of 10 cm (4 inches) precision; characteristics of the altered return pulse indicate surface roughness.
Lasers are also reliable and very accurate tools for determining distances to satellites in orbit. Retroreflectors are small prisms (typically quartz) mounted on the spacecraft. Even at their high orbital speeds, these spacecraft can be targeted to intercept a laser beam pulse directed at them from Earth-based stations which is then bounced back by the reflectors. Along with GPS, this is one way in which the orbital position of a satellite can be precisely fixed. The astronauts in later Apollo missions left retroreflectors on the Moon's surface as a means of learning more about its orbital motions, including its recession from Earth.
From space, real aperture microwave (radar) altimeters have served to measure various aspects of sea state, such as heights relative to the geoid, wave geometries, sea ice, and, indirectly, circulation characteristics such as currents and eddies. Like lasers, the signals are dispatched as short pulses, but at the longer radar wavelengths these signals can penetrate cloud cover. Again, using roundtrip times the instrument acts as a ranger to determine distance to target. Radar altimeters designed to secure data from the ocean surface use small antennas that dispatch long wavelength pulses through a wide beam that produces a broad footprint whose size is determined by pulse length. This pulse-limited type operates best on smooth surfaces but analysis of the degree of "stretching" of backscattered pulses (echoes) yields information on surface wave heights (roughness). For land measurements, especially on surfaces of high relief, the beam-limited altimeter requires a larger antenna (a practical limitation) capable of generating a narrow beam (hence, smaller footprint that better discriminates changes in slope) and shorter wavelengths. The orbital position of the sensor platform must be determined with high precision and accuracy to establish the position of the geoid and local departures of the surface from it; modifications of the signal by the atmosphere need to be accounted for, usually through corrections made from data acquired by an accompanying radiometer.
The first spaceborne altimeter experiment was conducted during the 1973 Skylab mission. Next was GEOS-3 (Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite) in 1975 which measured height differences greater than 60 cm. This was followed in 1978 by JPL's Seasat (which failed after 99 days but in the interim returned extremely valuable data over sea and land). Its altimeter, one of five instruments including a SAR, performed at 10 cm range precision. Among its remarkable products was a map of the morphology of the ocean floor, reproduced here:
The actual data source for this was the global map of sea surface elevation, which was digitally adjusted to remove effects of the lunar and solar tides and further corrected for bathymetric variations. What appears to be a topographic expression of the floor is actually the distortion of the surface gravitational field, expressed as broad variations in sea surface heights, as controlled by subsurface mass variations and their distribution under variable floor relief. Discernible are the many transform fault zones in the ocean plates, along with spreading ridges, trenches, and seamounts.
An instrument with performance similar to Seasat was mounted on the 1985 Geosat, launched by the Dept. of Defense as a geodetic surveyor. That same year planning and developed was begun on the TOPEX/Poseidon mission, operated jointly by NASA/JPL and CNES (Centre National d'Etude Spatiales) which was eventually launched with great success in August, 1992. Its dual frequency altimeter (13.6 Ghz and 5.3 Ghz [to make ionospheric corrections]), and a three-channel mirowave radiometer (to make tropospheric water vapor corrections) execute an average of 50000 observations/day over a latitudinal band of ± 63.1°. Wave heights as small as 4.3 cm (1.6 inches) can be detected. TOPEX/Poseidon has produced global maps that show seasonal variations in sea level brought on by the expansion of water from changes in regional temperatures (the outer 3 meters (~10 ft) of ocean water contains as much heat as the entire atmosphere). An example appears here:
These data sets can also be interpreted to follow changes in ocean current circulation (generally poleward currents) controlled by thermal upwelling, winds, and the Coriolis force, as well as effects of tides, development of eddies, and monitoring of El Niño (the equatorial shifts of waters owing to thermal influences). All of these observations bear on major aspects of global climate changes.
Space imagery can be acquired in modes suited to stereo viewing and, in principle, to analysis and contour mapping by stereoplotters. Radar images are capable of displaying the 3-D effect but this is usually not as "realistic" as aerial photography owing to layover, range effects, and other distortions (see Section 8).
Code 935, Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA
Written by: Nicholas M. Short, Sr. email: nmshort@epix.net
and
Jon Robinson email: Jon.W.Robinson.1@gsfc.nasa.gov
Webmaster: Bill Dickinson Jr. email: rstwebmaster@gsti.com
Web Production: Christiane Robinson, Terri Ho and Nannette Fekete
Updated: 1999.03.15.